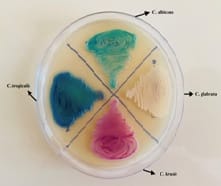
miological purpose and laboratory diagnosis[8].Hicrome Candida differential agar medium accurately identifies the important Candida species namely C. Albicans, C. tropicalis, C. glabrata, C. dubliniensis, and C. krusei based on their color and morphological features [9].
Fromthe present study, the rate of isolation of NAC was 50.8% and the isolation rate of C.Albicans was 49.2%. Non-albicans Candidapredominated over C
Albicans which correlates well with many other studies. In a study done by Kaup S et al[10], the Non-albicans Candida accounted for 50% of the isolates and the commonest species was C. Albicans (50%) followed by C. tropicalis (27.08%). Non-albicans Candida(52.8%) isolates were more than C. Albicans(47.2%) in a study by Samyuktha AA et al[11]Predominance of Non-albicans Candida(54%) over C. Albicans(46%) was also shown in a study by Madhumathi B et al[12].The present study also correlated with the study done by Marak MB et al [13] where the rate of isolation of Non-albicans Candida was 54.5%.
Though Candida albicans is considered to be the commonest species causing human diseases, there is a striking increase in the isolation rate ofNon-albicans Candidaspecies, primarilyCandida tropicalis, Candida glabrata, Candida krusei, and Candida parapsilosis. This rise in Non-albicans Candida species has been associated with significant morbidity and mortality [14]. Hence, identification of Candida upto species level becomes necessary for the initiation of early and effective therapy. As NAC species significantly vary in their prevalence among different countries and health-care setups within a country, species identification plays an important role in the formulation of local therapeutic guidelines [15].
In routine diagnostic laboratories,Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) iswidely used for the isolation of all yeast species from a clinical specimen. Sabouraud dextrose agar is not a differential medium, and multiple yeast growth cannot be easily distinguished from each other. In the majority of the laboratories germ tube test is used to differentiate C. Albicans and C. dubliniensis from other Candida species. Although it is a rapid test, it may lead to false positive and false negative results [16].The other conventional methods like sugar fermentation and sugar assimilation tests used for the speciation of Candidaare very time consuming and cumbersome. Molecular methods are very expensive
and available only at reference centers.
Chromogenic agar is a rapid method to differentiateCandidaspecies asit contains enzymatic substrates that are linked to chromogenic compounds. When a specific enzyme cleaves the substrate, the chromogenic substances produce color. The action of different enzymes produced by yeast species results in color variation which is useful for the presumptive identification of some
yeasts [14]. Another important advantage of chromogenic medium is it greatly facilitates the detection of specimens containing a mixture of yeast species though there were no mixed cultures in the present study. The prompt detection of such clinical scenarios of multiple yeast etiology may be an aid for early appropriate treatment decisions [16].
In the present study, amongst the NACmost frequently isolated species was C.tropicalis followed by C. glabrata and C. krusei. Many other studies have also shown the preponderance of C. tropicalis over other NACspecies [17,18,19,20,21,22,23].
Limitations of the study
Conventional methods for the identification of Candida species like sugar fermentation and assimilation tests are not included in the present study. Hence, other species of Candida like C. guilliermondii, C. parapsilosis, C. kefyr could not be identified in the present study.
Conclusion
Identification of Candida up to species level is very important in the early management of Candidiasis. Non-albicans Candida species are increasingly associated with invasive Candidiasis and differ from C. Albicans with respect to epidemiology and antifungal susceptibility.The present study highlights the fact thatNAC has emerged as an important cause of infections even in our set up and can no longer be ignored as non-pathogens and contaminants.
What does the study add to the existing knowledge?
The current study results are also important for local monitoring of different Candida species which also helps in planning empirical therapies.Hicrome agar is a simple, rapid,and inexpensive method for


 ©
©