Tobacco consumption is a very significant risk factor for oral cancers. Other risk factors are age and male sex. The risk increases further when combined with
alcohol. In the present study number of patients gave a history of tobacco consumption in the form of smoking or smokeless tobacco i.e. tobacco chewing. This finding was observed by other workers also.
In the present study, 81.67% of cases of well-differentiated (Grade I) squamous cell carcinoma, 15% of cases of moderately differentiated SCC, and 3.33% poorly differentiated SCC were observed. These findings are consistent with the findings of Atrametal [18].
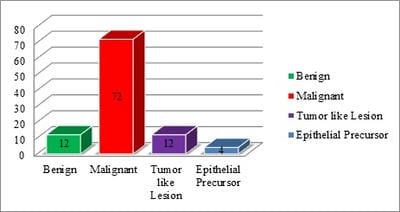
In the present study, the most common malignancy was squamous cell carcinoma (83.33%), followed by verrucous carcinoma (6.94%). We found 1 case (1.38%) each of the basaloid variant of squamous cell carcinoma, a spindle cell variant of squamous cell carcinoma and rhabdomyosarcoma. 2 cases (2.78%) each of mucoepidermoid carcinoma and Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma were studied. Ahluwalia et al [9] studied 2232 malignant cases of the oral cavity in which they found 2066 cases of SCC, 40 cases of the basaloid variant of squamous cell carcinoma, 4 cases each of lymphoma and mucoepidermoid carcinoma. They also found cases of basal cell carcinoma (66 cases), giant cell tumor (2 cases), adenoid cystic carcinoma (5 cases).
In the study of Parkins et al [5] most common malignancy was SCC (62%), followed by lymphoma (19%). They also studied cases of MEC (1%), chondrosarcoma (3%), adenocarcinoma (3%), spindle cell carcinoma (3%), ameloblastic carcinoma (1%) and plasmacytoma (1%). The incidence of NHL was higher in the study of Parkins et al (19%) due to the higher prevalence of Burkitts lymphoma in Ghana.
In the study of N. Riaz et al [6] most common malignancy was SCC (%), followed by salivary gland malignancies (16.1%). They also studied cases of chondrosarcoma (2%), rhabdomyosarcoma (5.3%), spindle cell carcinoma (3%), ameloblastic carcinoma (1%), and osteosarcoma (3.2%). Parikh et al [13] studied 81 cases of malignant lesions.
They found 71 cases of SCC, 7 cases of verrucous carcinoma, one case each of papillary SCC, adenoid cystic carcinoma and spindle cell sarcoma. In the study of Masamatti et al [16] SCC was the commonest malignancy (92.74%) followed by
verrucous carcinoma (4.55%). They also studied papillary carcinoma (0.60%), basaloid SCC (1.21%), spindle cell SCC (0.60%). Gupta et al [17] studied 162 cases of SCC, 2 cases of MEC, and 1 case of adenoid cystic carcinoma. Atram et al [18] studied 144 malignant cases. SCC was the commonest malignancy (135 cases). They also found 5 cases of verrucous carcinoma, 2 cases each of basaloid SCC, and rhabdomyosarcoma.
In the present study 4 cases of dysplasia were studied. Peak age incidence in the 5th decade was noted. All 4 cases were male. The most common site as buccal mucosa followed by tongue and gingiva. Clinically the lesion was presented as white (leukoplakia) or red (erythroplakia) patch.
In the present study incidence of premalignant lesions was 4 %. This correlates with studies of Parikh et al [13], Masamatti et al [16], and Gupta et al [17]. A higher incidence was noted in the study of Mehrotra et al [2] (29.89%). In the study of Mehrotra et al [2] among 344 cases of premalignant lesions, 73.2% were male and 26.7% were females. Gupta et al [17] studied 8 cases of premalignant lesions.
The peak age of incidence was in the 5th decade. 6 cases were makes and 2 were females, the most common site of involvement was buccal mucosa. In the study of Masamatti et al [16] 30 cases of premalignant lesions were studied, 19 were males and 11 were females with peak age incidence in the 5th decade. Clinically these lesions were presented as mucosal irregularities and white patches. The most common site of involvement was buccal mucosa followed by tongue.
The present study was hospital-based and not community-based.
Hence results may vary due to patient selection bias. In the present study we studied 12 benign lesions, most common benign lesion was squamous papilloma (5 cases, 41.67%) followed by haemangioma (4 cases, 33.33%). Two cases of granular cell tumors and one case of chondroma of hard palate were studied. Parikh et al [13] found 3 benign lesions, 2 cases of squamous papilloma, and 1 case of Neurofibroma.
Gupta et al [17] found 5 cases of squamous papilloma, 3 cases of haemangioma, 2 cases of pleomorphic adenoma, and 1 case of basal cell adenoma, fibroma, lipoma, Neurofibromaandschwannoma. Atram et al [18]


 ©
©