Comparative Peripheral Nerve Conduction Study of Median and Ulnar nerves in Type-2 Diabetics with Age and Sex Matched Normal Subjects.
Bhagya V.1*, Brid SV.2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/jopm.2021.i05.01
1* Bhagya V, Professor, Department of Physiology, JJM Medical College, Davanagere, Karnataka, India.
2 Brid SV, Professor, Department of Physiology, SN Medical College, Bagalkot, Karnataka, India.
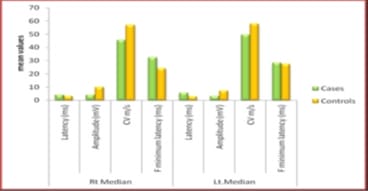
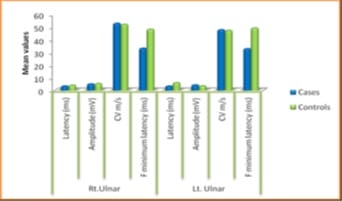
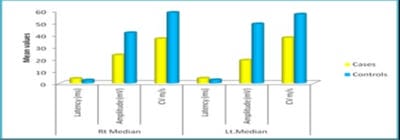
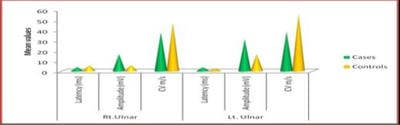
Background: Diabetes Mellitus affects the peripheral nervous system, and in uncontrolled diabetes, symptomatic neuropathy is one of the commonest incapacitating complications. Diabetic neuropathy can be detected at an early stage using Electrodiagnostic tests. Nerve Conduction Study (NCS) is the most sensitive, reliable, non-invasive and objective means of investigations of Diabetic Polyneuropathy. If detected, the proper treatment can be instituted in the early stages with a good outcome. As the peripheral nerve can regenerate, a line of treatment can be planned accordingly. Based on this background, the present study aimed to evaluate the comparative peripheral nerve conduction study of median and ulnar nerves in people with type-2 diabetes with polyneuropathy. Methods: A total of 58 subjects were included in the present study, 29 subjects with Diabetic Neuropathy and 29 age and sex-matched healthy subjects. Motor and Sensory nerve conduction studies were conducted in both upper and lower limbs nerves using bipolar surface electrodes with RMS EMG EP MARK-II machine. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS 20.0. Results: A definite decrease in amplitude and nerve conduction velocities of both the sensory and motor components, axonal and demyelinating type, significantly correlating with higher HbA1c levels. F minimum latencies of Median nerves were increased, possibly more of demyelinating type of polyneuropathy. Conclusion: NCS being a simple, harmless, non-invasive and objective technique along with the easy interpretation of results, can be used routinely to evaluate the status of nerves in patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus to prevent a more disabling state the earliest.
Keywords: Diabetic Polyneuropathy, Nerve Conduction Study, HbA1c
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Professor, Department of Physiology, JJM Medical College, Davanagere, Karnataka, India. Email: |
Bhagya V, Brid SV, Comparative Peripheral Nerve Conduction Study of Median and Ulnar nerves in Type-2 Diabetics with Age and Sex Matched Normal Subjects.. Trop J Pathol Microbiol. 2021;7(5):219-225. Available From https://pathology.medresearch.in/index.php/jopm/article/view/574 |


 ©
©