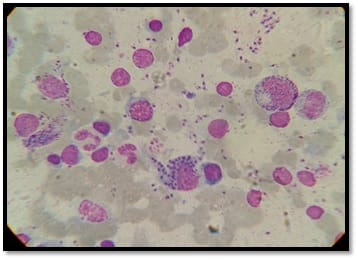
Manifestations of Bone Marrow Abnormalities of HIV/AIDS Patients
Kanti Pramanik S.1*, Guha Mallick Sinha M.2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/jopm.2021.i03.05
1* Soumya Kanti Pramanik, Post Graduate Trainee, Department of Pathology, Institution of Post Graduate Medical Education & Research, Kolkata, West Bengal, India.
2 Mamata Guha Mallick Sinha, Professor and Head, Department of Pathology, Institution of Post Graduate Medical Education & Research, Kolkata, West Bengal, India.
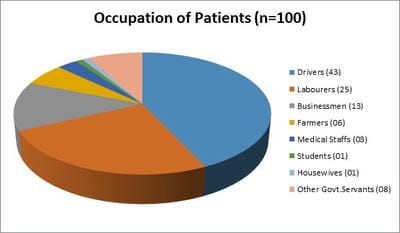
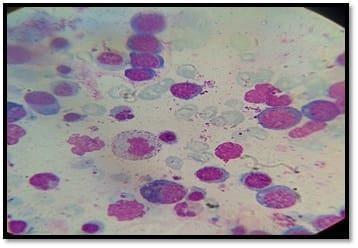
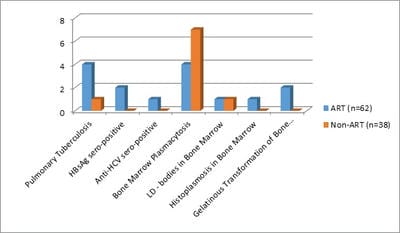
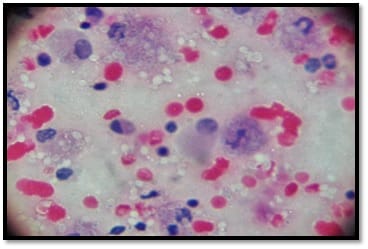
Background: Human immunodeficiency virus can involve almost any organ system. Anemia is the most common hematological manifestation in HIV/AIDS patients. Bone marrow changes include varying degrees of dysplasia in one or more cell lines, plasmacytosis, opportunistic infections and hematological malignancies. There are only a few studies where hematological manifestations of HIV/AIDS patients had been described. Materials and Methods: 100 HIV positive patients, aged between 12-65 years were enrolled in this hospital-based cross-sectional study. The study was conducted from March 2016 to March 2018. A complete blood count, CD4 counts were done, besides a thorough history and clinical examination. HIV positive patients were classified as those having AIDS and Non-AIDS, according to NACO criteria. Written informed consent was taken from patients and bone marrow aspiration was done. Results: Total number of patients included in the study was 100. We were able to do a CD4 count of 91 patients. As per criteria, out of 91 patients, 37 cases had AIDS. The most common hematological abnormality was anemia, seen in 95.45%of patients. Bone marrow was normocellular in 86.48% of AIDS and 85.18% of non-AIDS, hypocellular in 8.10% of AIDS and 9.25%o f non- AIDS, hypercellular in 5.40% of AIDS and 5.55% of non-AIDS patients. Dysplasia was statistically and significantly associated with anemia. The commonest dysplastic features are seen in the granulocytic and erythroid series. L.D. bodies were seen in 2 cases and Histoplasma was found in one case. Conclusion: Normocytic normochromic anemia was the most common peripheral smear finding. Hypocellular bone marrow was more common than hypercellular marrow in an advanced stage of the disease. Dysplastic changes were more common in AIDS than Non-AIDS. Granulocytic dysplasia was the most common type of dysplasia. There was evidence of opportunistic infections and gelatinous transformation were detected in our study.
Keywords: Hematology, Bone marrow, Myelodysplasia, Leishmaniasis, Histoplasma, Gelatinous transformation, HIV
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Post Graduate Trainee, Department of Pathology, Institution of Post Graduate Medical Education & Research, Kolkata, West Bengal, India. Email: |
Pramanik SK, Sinha MGM. Manifestations of Bone Marrow Abnormalities of HIV/AIDS Patients. Trop J Pathol Microbiol. 2021;7(3):119-127. Available From https://pathology.medresearch.in/index.php/jopm/article/view/536 |


 ©
©