Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) – A useful parameter to assess prognosis in COVID patients
Sahai J.1*, Prabhakar P.2, Sahu S.3
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/jopm.2021.i02.03
1* Jyotsna Sahai, Resident, Department of Pathology, MGM Institute of Health Sciences, Navi Mumbai, Maharastra, India.
2 Patro Prabhakar, Professor, Department of Pathology, MGM Institute of Health Sciences, Navi Mumbai, Maharastra, India.
3 Shilpi Sahu, Professor and Head, Department of Pathology, MGM Institute of Health Sciences, Navi Mumbai, Maharastra, India.
Background and Objectives: The world is currently grappling with the COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, it is important to identify reliable and cost-effective biomarkers that can help in triage and early detection of severe patients, thus preventing morbidity and mortality thereby reducing the need for invasive and critical care management. With this study, we aimed to observe --
1) Variations in red cell distribution width (RDW) in survivors and non – survivors of COVID – 19.
2) If there is an association between elevated RDW and unfavourable outcome in patients.
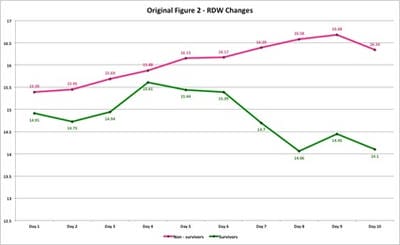
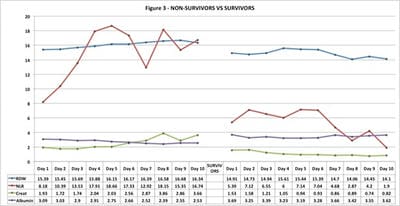
3) If there was an association between RDW and currently used biomarkers. Method: A retrospective study was conducted from June – August 2020 on 100 RTPCR confirmed patients, with 50 admitted in ICU (non-survivors) and 50 in isolation wards (survivors). Eight laboratory parameters with their changes were monitored daily on all patients. Results: We found that all eight parameters (RDW, CRP, LDH, Albumin, WBC count, Ferritin, Creatinine, NLR) were markedly deranged among non-survivors as compared to survivors. A male preponderance was found in the study. RDW values progressively increased in non-survivors till the end of the observation period and indicated unfavourable outcome sooner. In survivors, RDW showed minimal variation throughout the observation period. The RDW values were not affected by complications arising due to COVID-19 infection or by therapy as compared to other biomarkers. Conclusions: RDW showed a direct relationship with other commonly used biomarkers and can be successfully used in triage and treatment of mild, moderate and severe Covid-19 patients.
Keywords: Biomarker, COVID-19, Laboratory, Non-Survivors, Parameters, RDW, Survivors
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Resident, Department of Pathology, MGM Institute of Health Sciences, Navi Mumbai, Maharastra, India. Email: |
Sahai J, Prabhakar P, Sahu S. Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) – A useful parameter to assess prognosis in COVID patients. Trop J Pathol Microbiol. 2020;7(2):78-84. Available From https://pathology.medresearch.in/index.php/jopm/article/view/520 |


 ©
©