Evaluation of markers of thrombosis and fibrinolysis in malaria patients in tertiary care hospital in Central India
Chouhan S.1*, Gautam Singh S.2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/jopm.2020.i08.07
1* Swati Chouhan, Consultant, Department of Pathology, Apex Hospital, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India.
2 Siddharth Gautam Singh, Senior Resident, Department of E.N.T, ESIC Hospital, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India.
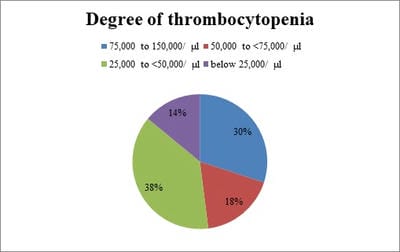
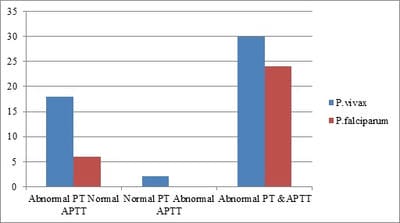
Background: Cases of malaria are known to be associated with variable degrees of coagulopathy as evident from abnormalities of screening coagulation assays in a large number of patients during the illness. However, attempts to use laboratory parameters as indicators of the severity of the underlying coagulopathy and for monitoring disease progression have met with only partial success. Methods: This prospective study was conducted in the department of Pathology in Ruxmaniben Deepchand Gardi Medical College, Ujjain. Blood samples of all the patients diagnosed positive with malaria were collected in vials containing ethylene tetra-acetic acid tri potassium salt for hematological parameters and in trisodium citrate tubes for coagulation assays. Result: Out of the total positive cases, PT was prolonged in 65% of total cases, Percentage positivity for prolonged PT for falciparum and vivax is 60% and 68.5% respectively. APTT has raised 47% of malaria positive cases with percentage positivity for falciparum and vivax 48% and 45.7% respectively. 55% of total cases showed raised levels of fibrin degradation products, which included 48% of falciparum cases and 60% of vivax cases. Out of 120 positive cases of malaria, D- Dimer was raised 41.7% cases. Conclusion: As blood is the chief component affected by malaria, not only proper examination of peripheral smears is required for detection and species identification, but a careful evaluation of other laboratory parameters should be done irrespective of the malarial species for the early diagnosis of compensatory and non-compensatory consumptive coagulopathy.
Keywords: Malaria, Fibrinolysis, Platelet, Fibrin degradation product
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Consultant, Department of Pathology, Apex Hospital, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India. Email: |
Chouhan S, Singh SG. Evaluation of markers of thrombosis and fibrinolysis in malaria patients in tertiary care hospital in Central India. Trop J Pathol Microbiol. 2020;6(8):498-503. Available From https://pathology.medresearch.in/index.php/jopm/article/view/490 |


 ©
©