A study on prevalence of plasmid mediated quinolone resistant genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae
Priyadharsini R I.1, Rao A V.2*, Kavyashri J.3
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/jopm.2019.i07.02
1 Indra Priyadharsini R, Professor and HOD, Department of Microbiology, VMKV Medical College and Hospital, Vinayaka Missions Research Foundation (Deemed to be University), Salem, Tamil Nadu, India.
2* Venkata Raghavendra Rao A, Assistant Professor, Department of Microbiology, VMKV Medical College and Hospital, Vinayaka Missions Research Foundation (Deemed to be University), Salem, Tamil Nadu, India.
3 Kavyashri J., Final year Postgraduate student, Department of Microbiology, VMKV Medical College and Hospital, Vinayaka Missions Research Foundation (Deemed to be University), Salem, Tamil Nadu, India.
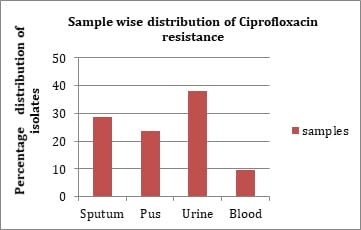
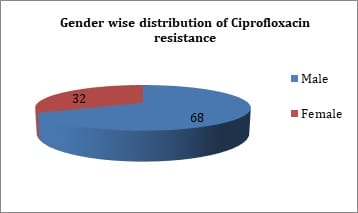
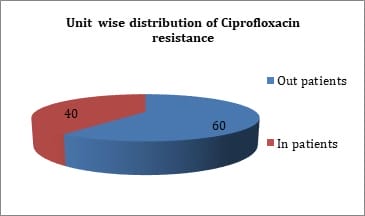
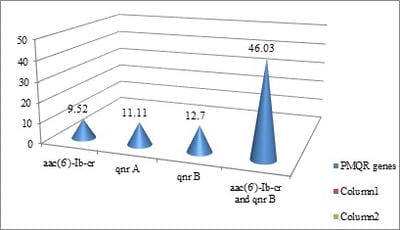
Introduction: Fluoroquinolone resistance is increasingly been reported in Enterobacteriaceae. Resistance to quinolones among Enterobacteriaceae is mediated by point mutations in chromosomal genes that encode the subunits of DNA-gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Objectives: The present study was done to identify quinolone resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from clinical samples and to detect the prevalence of plasmid mediated quinolone resistance genes. Materials & Methods: A total of 63 isolates from various clinical samples were identified by standard biochemical methods. Antimicrobial resistance pattern of these isolates were performed by disk diffusion method as per guidelines of CLSI. Results: By disk diffusion, 90.99% isolates were found to be resistant to Ciprofloxacin. The sensitivity of isolates to Imipenem was found to be 99.10%. About 50.74% isolates were resistant to Aminoglycosides and 61.19% were resistant to third generation Cephalosporins. By E test, 80.95% isolates were resistant for Ciprofloxacin with MIC of >1µg/ml. By PCR, out of 63 isolates, 6 (9.52%) showed aac (6’) – Ib - cr gene, 7 (11.11%) were positive for qnr A gene, 29 (46.03%) for both qnr B and aac (6’) - Ib-cr gene and 8 (12.70%) for qnr B gene. Conclusion: The transferrable nature of Plasmid mediated fluoroquinolone resistant genes favours the dissemination of the resistant genes between different bacterial genera and limit therapeutic options available. The prevalence of plasmid mediated quinolone resistance mediated by qnr A, qnrB and aac (6’) - Ib-cr gene results in multidrug resistance among Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Keywords: Fluoroquinolone resistant genes, Klebsiella pneumoniae, E test, High level quinolone resistance
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Assistant Professor, Department of Microbiology, VMKV Medical College and Hospital, Vinayaka Missions Research Foundation (Deemed to be University), Salem, Tamil Nadu, India. Email: |
Priyadharsini RI, Raghavendra Rao AV, Kavyashri J. A study on prevalence of plasmid mediated quinolone resistant genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Trop J Pathol Microbiol. 2019;5(7):420-430. Available From https://pathology.medresearch.in/index.php/jopm/article/view/283 |


 ©
©